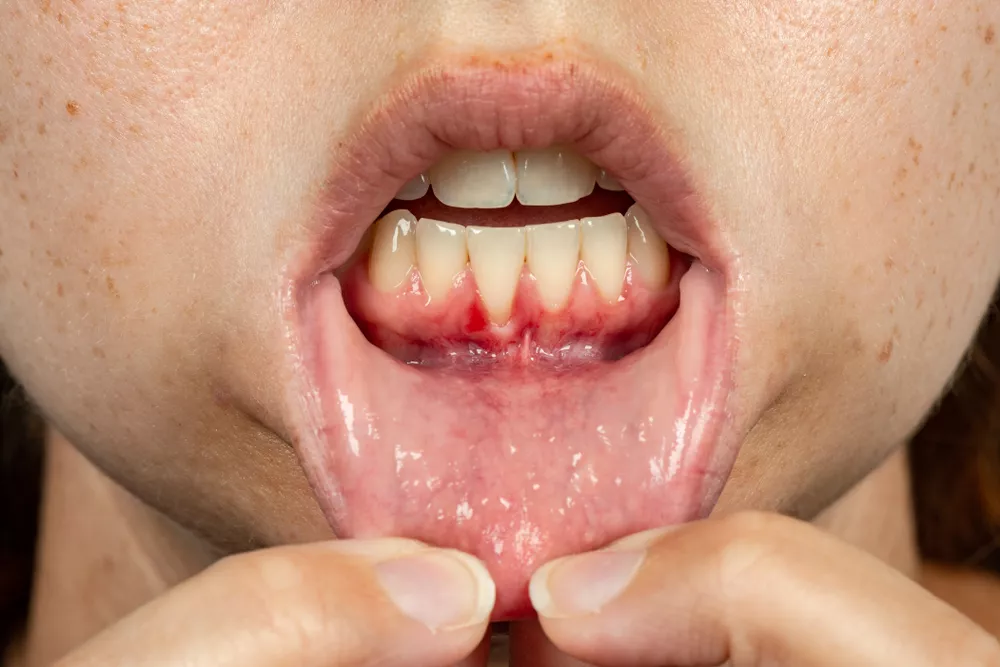
Gums are supporting soft tissues that surround your teeth, providing anchorage. They are properly scalloped, providing an aesthetic appearance to your smile. Any discrepancy in the shape of your gum line can be displeasing due to exposure of your tooth roots.
Our renowned dentist in Salina, Kansas, and the team are dedicated to providing you with quality dental treatment to enhance your gums. They help to restore and accentuate the beauty of your smile.
Gum recession explained
Gum recession is a clinical term for receding gums. The margins of the gum tissue encircling the teeth wear away or pull back, exposing the tooth roots. This leads to a deep space between the gums and the tooth surface, known as a gingival pocket. These pockets favor an increased accumulation of plaque and bacterial colonization.
If not treated promptly, the bacterial infection can spread and can damage the underlying bone, eventually leading to tooth loss.
Potential causes that contribute to gum recession
There are several factors that cause your gums to recede, such as:
- Genetic predisposition
- If a member of your family suffers from gum recession, it is passed down through generations.
- Periodontal disease
- Bacterial infiltration can erode the gums, leading them to detach and recede from the tooth surface, exposing the roots.
- Aggressive tooth brushing
- Using a hard-bristled toothbrush with extreme force can damage the gums.
- Poor oral care
- Inadequate brushing, flossing, or rinsing with an antibacterial mouthwash favors excess plaque buildup.
- Hormonal changes
- Women are prone to hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy or menopause, which leads to the hardening of plaque into calculus.
- Tobacco use
- Tobacco can release harmful toxins that irritate the gingival lining.
- Bruxism
- Excess clenching or grinding of the teeth can exert too much force on the teeth, causing gums to recede.
- Malalignment
- Crooked, crowded, and malaligned teeth can favor plaque accumulation and make brushing and flossing challenging.
Clinical features associated with gum recession
The most striking feature of gum recession is the exposure of tooth roots. Other warning signs include:
- Pain near the gum line
- Extreme sensitivity to hot and cold
- Discomfort while brushing and flossing your teeth
- Teeth appear longer than usual
- Gingival bleeding
- Halitosis (bad breath)
Managing gum recession
Treatment usually depends on the cause of the condition. The options include:
Conservative approach
- Topical antibiotics to treat infection
- Scaling and root planing to eliminate plaque and calculus
- Dental bonding to camouflage the area of recession for cosmetic purposes
- Orthodontics for crooked teeth
Surgical intervention
- Gum grafting helps to replace your missing gum tissue
Failure to detect the cause of gum recession and manage it on time can be catastrophic to your oral health, leading to several complications.


Comments are closed.