Cardiovascular myxoma according to the Lecturio Medical Library is the most well-known of the essential growths of the grown-up heart, which are all exceptionally uncommon. Cardiovascular myxoma is a harmless neoplasm that emerges from crude multipotent mesenchymal cells. Most happen irregularly, however some are a piece of some familial disorders. Every one of the 4 chambers might lead to myxoma, yet 90% begin and fill in the atria, with a left-to-right proportion of around 4:1. Determination is made by echocardiography, cardiovascular attractive reverberation imaging (MRI), or heart figured tomography (CT). Complete careful extraction is required as a result of the significant danger of embolization and cardiovascular intricacies, including abrupt passing.
Outline
Definition
Cardiovascular myxoma is a harmless essential cancer of the heart.
The study of disease transmission
Essential heart cancers are exceptionally uncommon: frequency < 0.1%
Myxoma is the most well-known essential heart cancer.
Generally normal in grown-ups, however can occur in all age gatherings
90% of heart myxomas emerge in the atria, with left-to-right proportion of 4:1.
Ladies > men
Most are inconsistent.
Most normal acquired structure is a piece of Carney complex:
Autosomal predominant problem:
Atrial and extracardiac myxomas
Schwannomas
Pigmentation irregularities
Endocrine and different cancers
Not as old as group of three or Carney-Stratakis disorder
Etiology
Emerges from crude multipotent mesenchymal cells
No reliable hereditary adjustments in inconsistent myxomas
Development variables might add to cancer arrangement, e.g., vascular endothelial development factor (VEGF), an angiogenic factor.
Familial disorders with myxomas are related with explicit hereditary imperfections:
Carney complex: invalid changes in PRKAR1A, encoding an administrative subunit of a cyclic-AMP–subordinate protein kinase
Mazabraud’s condition: single or numerous intramuscular myxomas with sinewy dysplasia; enact changes in the GNAS1 quality
Pathophysiology
Life structures and histology
80% begin in the left chamber (most normally, fossa ovalis).
Most others are in the right chamber.
Reach from 1–15 cm in width
Ordinarily pedunculated growths with gelationous consistency
Tiny provisions:
Dispersed stellate or globular cells in the mucopolysaccharide stroma
Can be joined by discharge and persistent aggravation
Little cancers will in general be villous and friable.
Bigger cancers generally have a smooth surface.
Pathophysiologic instruments
Check of blood stream: causes cardiovascular breakdown
Obstruction with cardiovascular valves:
More normal with pedunculated myxomas
Spewing forth
Embolization:
More normal with little cancers (from parts or surface thrombi)
More usually foundational than pulmonic
Direct intrusion of the myocardium:
Left ventricular brokenness
Arrhythmias/heart block
Pericardial radiation
Attack of the neighboring lung (can impersonate cellular breakdown in the lungs)
Cytokine creation (e.g., interleukin-6)
Clinical Presentation
Left-side myxomas (roughly 85%)
Indications like mitral valve stenosis or spewing forth (left cardiovascular breakdown):
Dyspnea
Orthopnea
Paroxysmal nighttime dyspnea
Hack/hemoptysis
Edema
Exhaustion
Neurologic indications: optional to fundamental emboli
Arrhythmias
Right-side myxomas (around 15%)
Indications of tricuspid infection (right cardiovascular breakdown):
Exhaustion
Fringe edema
Hepatomegaly
Ascites
Syncope
Unexpected passing
Pneumonic embolism
In the event that patent foramen ovale is available:
Fundamental emboli
Hypoxemia (from shunting of venous blood from the right side)
Sacred side effects
Might be seen in 30% of patients
Cytokine discharge:
Fever
Weight reduction
Exhaustion
Conclusion and Management
Actual assessment
Left atrial cancers:
Diastolic “cancer thud” on auscultation
Pneumonic edema: rales or snaps on auscultation
Right atrial cancers:
Diastolic mumble
Jugular venous widening
Summed up edema
Hepatomegaly
Stomach ascites
Imaging
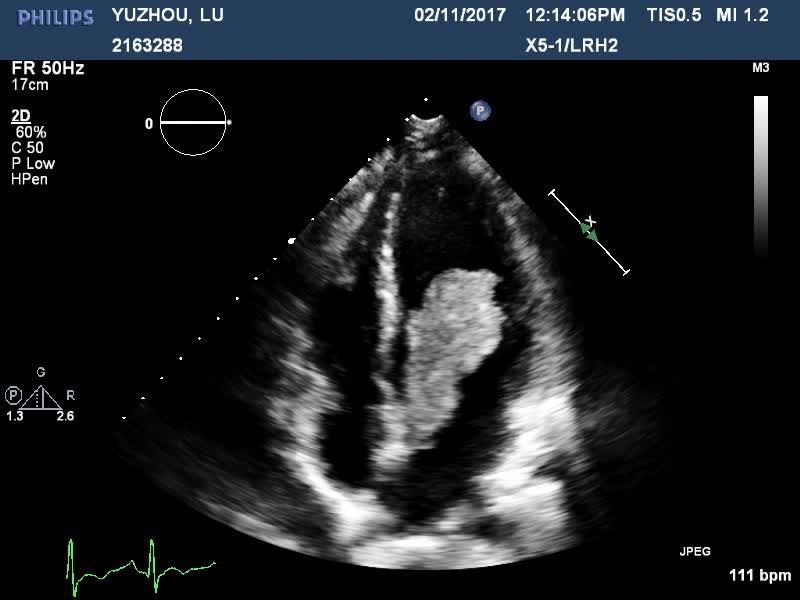
Echocardiography (typically first imaging method):
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) gives better goal.
Can typically recognize:
Mass
Portability
Deterrent
Embolization
Heart attractive reverberation imaging (CMR): point by point anatomic imaging
Heart figured tomography (CCT): if CMR not accessible
Positron discharge tomography (PET) check separates:
Metastatic cancers versus atrial myxoma
Lipomatous septal hypertrophy versus atrial myxoma
Coronary angiography:
“Ocean anemone” appearance on angiography
Planning of blood supply: might be required for careful arranging
Transvenous biopsy
Hazard of embolism
Ought to possibly be performed in case analysis is unsure and benefits offset the dangers
The board
Careful resection is required due to:
Hazard of embolization
Cardiovascular entanglements
Hazard of unexpected demise
Forecast:
Usable death rate < 5%
Repeat: 2%–5% of cases, more normal if familial or various
Heart autotransplantation (with atrial remaking) or transplantation might be essential for repetitive atrial myxoma.
Atrial arrhythmias or atrioventricular conduction irregularities in 26%
Differential Diagnosis
Harmless essential heart cancers or growth like masses
Intracardiac blood clot: the most well-known sort of intracardiac mass in grown-ups. May happen following myocardial localized necrosis with ventricular clots arrangement, or with atrial fibrillation and mitral stenosis where atrial thrombi prevail. Left-sided thrombi are a typical wellspring of stroke and other blood vessel embolic disorders. Ultrasound and CMR help in the analysis. Treatment is ordinarily with anticoagulation.
Rhabdomyoma: the most widely recognized pediatric cardiovascular cancer; a harmless neoplasm of muscle cells, frequently different, related with tuberous sclerosis. Much of the time goes through unconstrained relapse; determination is established by clinical connection and imaging.
Fibromas: second most normal essential pediatric heart growth. Made out of fibroblasts, which for the most part emerge in ventricular septum. Fibromas might be essential for Gorlin condition (nevoid basal cell carcinoma disorder); doesn’t relapse, however may not require treatment assuming little.
Lipomas: uncommon embodied neoplasm of mature fat cells. May begin from subendocardium, subpericardium, or from the myocardium. Lipomas are more regular in the left ventricle or right chamber.
Papillary fibroelastoma: the second most normal essential cardiovascular growth in grown-ups. Papillary fibroelastoma are little ocean anemone–formed endocardial growths with frond-like designs, for the most part on mitral or aortic valves, where they can make indications due embolization, both of the actual cancer or blood clot. Imaging is symptomatic, and medical procedure is suggested.
Threatening growths of the heart
Sarcoma: dangerous cancer beginning from the connective tissue cells. Incredibly uncommon in the heart. Angiosarcoma is the most widely recognized sort. Anticipation is poor, as these cancers will in general develop quickly and repeat in any event, when totally resected.
Metastatic cancers: multiple times more normal than essential growths. Might be available in 20% of patients passing on of malignancy. Side effects rely upon the site of heart association. Conclusion is made with echocardiography, CMR, or CCT.


Comments are closed.